Two-factor authentication is considered the most effective security method, but a new study says it may not be as safe as it seems. Cyber attacks come in many different forms which evolve as counter-cybersecurity measures advance. In the past, hackers used to rely on the victim’s actions, gaining access when they clicked on a link, filled out a form, or engaged in some way. But new attacks like zero-click and “man-in-the-middle” require no action by a user.
2FA authentication attacks are not new, but the methodology is. New attacks are becoming extremely sophisticated, effective, and dangerous. Facial recognition, biometrics, rotating keys, and password-less accounts are trying to replace 2FA, and one of the biggest problems with two-factor systems is that many users don't even bother to set them up.
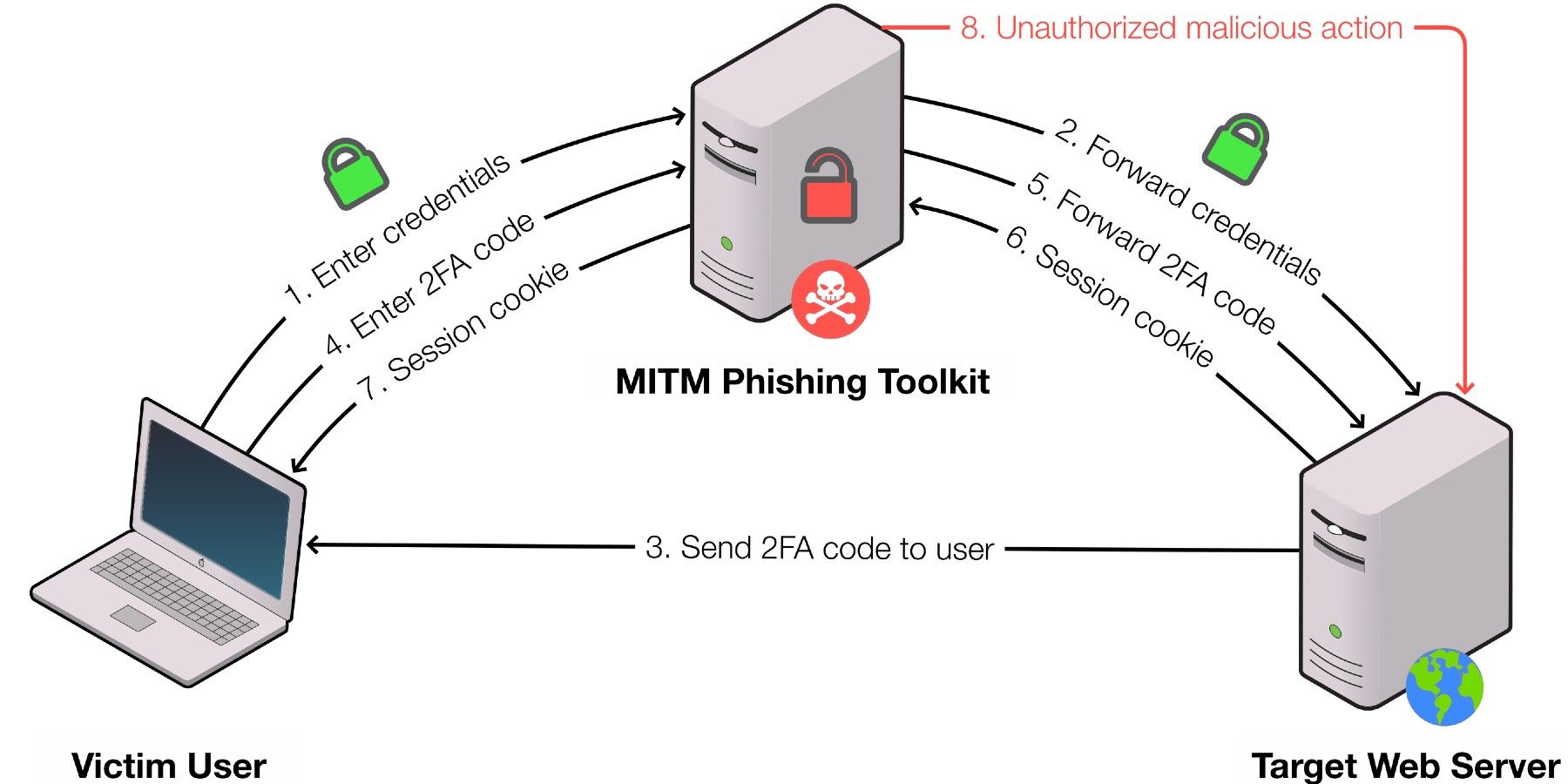
Researchers from the cybersecurity firm Palo Alto Networks and Stony Brook University have developed a machine learning classifier that beats new man-in-the-middle attacks. They explain that hackers are using this method to steal data while “mirroring” an online site that exchanges cookies with the victim. They concluded their security tool is 99.9 percent accurate. Surprisingly, they have captured data on 1,220 man-in-the-middle phishing websites.
Hackers Bypassing Phishing Blocklists
Researchers found that MITM phishing toolkits have managed to escape phishing blocklists. Only 43.7 percent of the domains and 18.9 percent of IP addresses they discovered are on blocklists. The team showed how average users, who are not experts, are vulnerable to these attacks. The hack can go on for months without the user ever noticing it because it happens while the user navigates to usual websites.
The detection program the team developed can outsmart the camouflage mechanisms that hackers are using in these new methods. Their tool can also be used to stop attacks as they happen. “MITM phishing toolkits are the state of the art in phishing attacks today,” the team says. The “no-action-required-to-be-hacked” trend continues to grow with new methods. MITM attacks can bypass JavaScript defenses and don’t go after passwords but after authentication cookies.
Which 2FA Method Is The Most Secure?
Two-factor authentication requires another level of authentication apart from a user's password. This is usually in the form of a unique code that is sent to the user, which they need to enter to gain access to a website or service. One way to get a secure code is through a text message sent to the user's primary phone number.
The more secure way is to use an authentication app. There are quite a few on the market, but the most popular ones include Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator, and Authy. Users can use any authentication app of their choice, and will need to link it to different accounts, such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc. When logging in to these apps, users will need to open the authenticator app which will display a code that's valid only for about 30 seconds. Both these methods require a user to have a phone with them, which can be inconvenient. While using two-factor authentication isn't a foolproof way to prevent hackers from accessing accounts, it's far safer than not enabling it in the first place.
Source: Catching Transparent Phish